- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

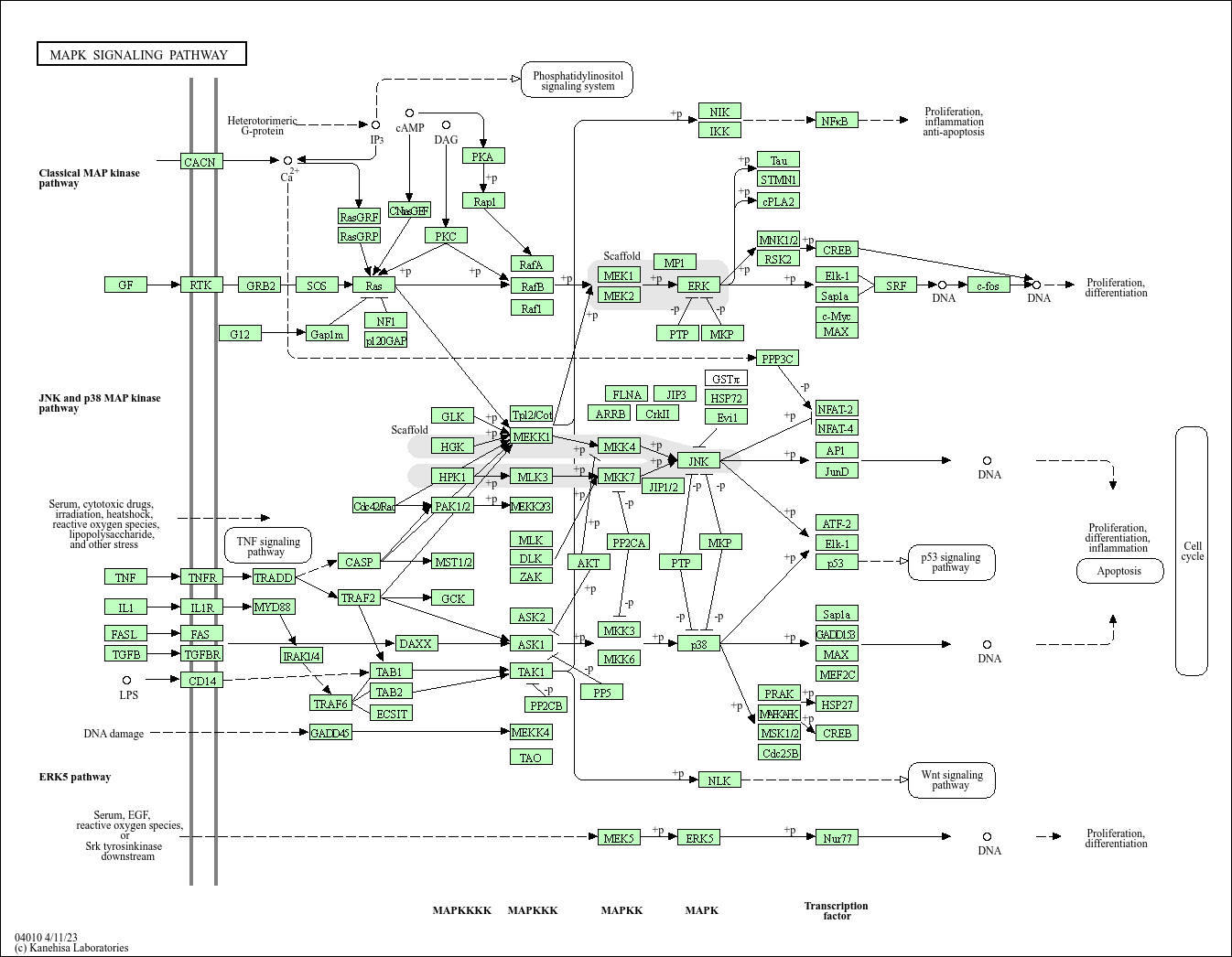
MAPK signaling pathway
A key intracellular signal transduction network that transmits various extracellular signals, including growth factors, cytokines, and stress stimuli (e.g., oxidative stress, ultraviolet radiation), through a three-tier kinase cascade (MAPKKK→MAPKK→MAPK). There are four main branches in mammals: ERK1/2 (regulating proliferation and differentiation), JNK (regulating apoptosis and inflammation), p38 (regulating stress response and differentiation), and ERK5 (regulating angiogenesis and cell survival). For example, growth factors activate the ERK1/2 pathway to promote cell proliferation; oxidative stress activates the JNK and p38 pathways to induce cell apoptosis or initiate stress adaptation. The pathway participates in multiple physiological processes such as embryonic development, immune response, and tissue repair. Abnormal activation is associated with tumors, inflammatory diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases, and inhibitors targeting MEK and ERK have been used in tumor treatment.
Core function: Transmit growth factor and stress signals through a three-tier kinase cascade to regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and migration. Key regulatory molecules: Ras, Raf, MEK1/2, ERK1/2, JNK, p38.
Core function: Transmit growth factor and stress signals through a three-tier kinase cascade to regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and migration. Key regulatory molecules: Ras, Raf, MEK1/2, ERK1/2, JNK, p38.
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us