- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

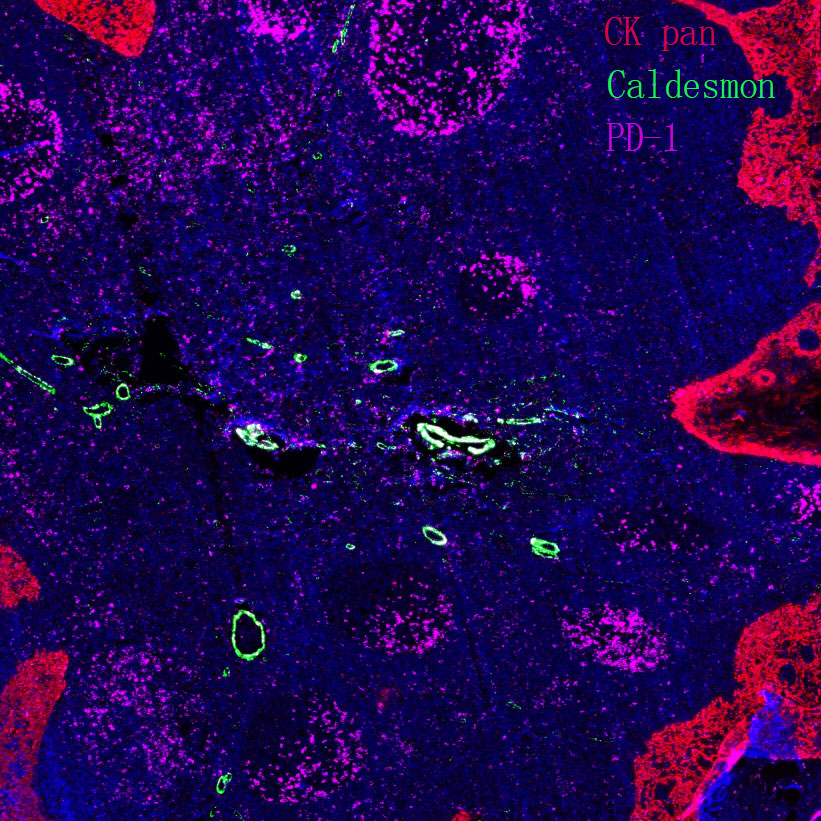
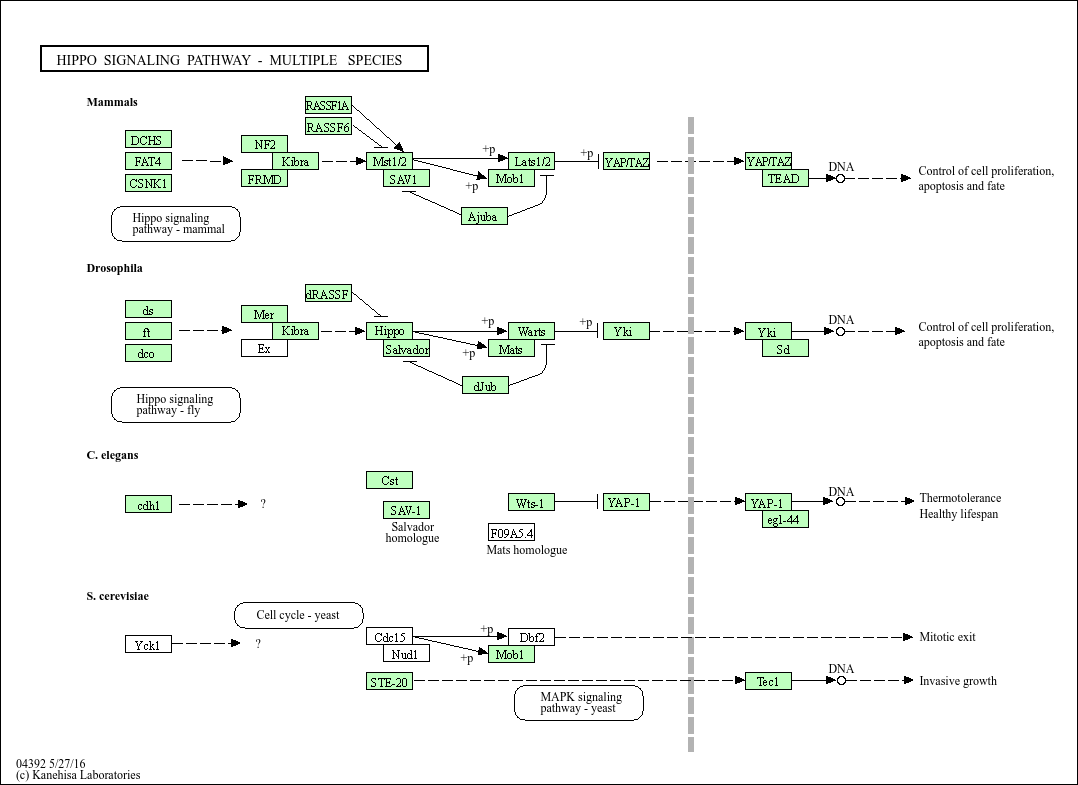
Hippo signaling pathway - multiple species
A cross-species conserved mechanism for regulating proliferation and differentiation, with homologous molecules and similar regulatory patterns existing from lower eukaryotes (e.g., Drosophila, C. elegans) to higher mammals. The core molecules in Drosophila, including Hpo (MST homolog), Wts (LATS homolog), and Yki (YAP homolog), have highly consistent functions with their mammalian counterparts and the same regulatory logic. The conservation of this pathway reflects its core position in life activities, providing convenience for studying the evolutionary origin of the pathway and analyzing basic regulatory mechanisms (e.g., using Drosophila models for rapid screening of pathway regulatory factors), and also providing an important basis for the construction of cross-species disease models (e.g., tumors, developmental malformations), facilitating cross-species validation of targeted drugs.
Core function: A cross-species conserved mechanism for proliferation and differentiation regulation, existing from lower organisms to higher animals and plants, with core functions consistent with single-species pathways. Key regulatory molecules: MST homologs, LATS homologs, YAP/TAZ homologs (e.g., Drosophila Yki).
Core function: A cross-species conserved mechanism for proliferation and differentiation regulation, existing from lower organisms to higher animals and plants, with core functions consistent with single-species pathways. Key regulatory molecules: MST homologs, LATS homologs, YAP/TAZ homologs (e.g., Drosophila Yki).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us