- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

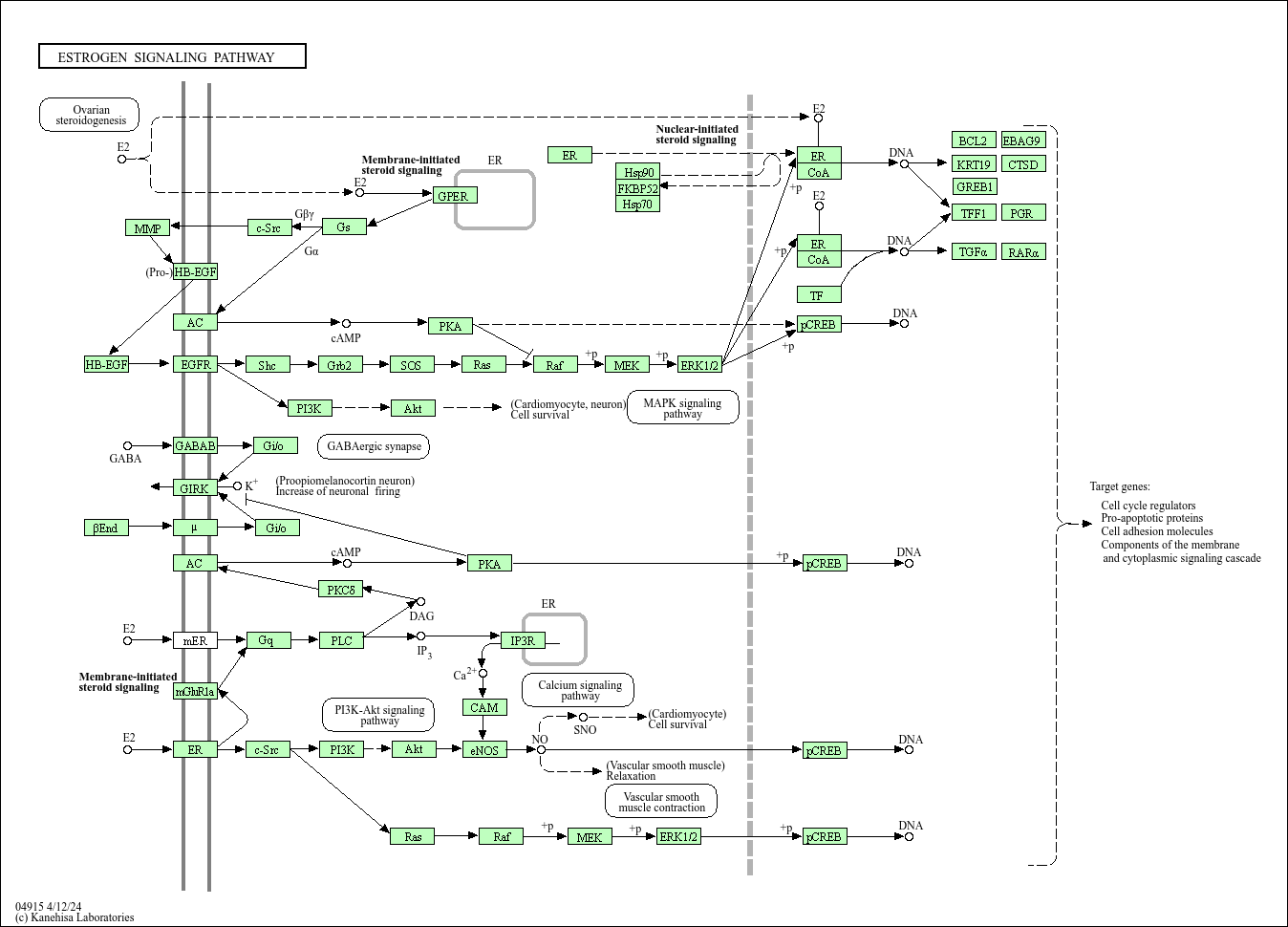
Estrogen signaling pathway
Core of basic research: Focuses on the molecular mechanisms by which estrogen (mainly E2) regulates reproductive development, bone metabolism, cardiovascular homeostasis, and cell proliferation/differentiation, including nuclear receptor-mediated genomic effects and membrane receptor-mediated non-genomic effects. Genomic effects: Estrogen binds to nuclear estrogen receptors (ERα/ERβ), forming heterodimers that bind to estrogen response elements (ERE) in target gene promoters, regulating the transcription of downstream genes (e.g., progesterone receptor PR, Cyclin D1) and participating in uterine development, breast hyperplasia, and bone formation. Non-genomic effects: Estrogen binds to the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER/GPR30) on the cell membrane, activating the PI3K-Akt and MAPK pathways to rapidly regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and calcium homeostasis. Research focuses on the tissue-specific functions of ERα/ERβ, the synergistic regulation of genomic and non-genomic effects, and pathway abnormalities associated with breast cancer, endometrial cancer, osteoporosis, and cardiovascular diseases.
Core key proteins: Estrogen (E2, 17β-estradiol), ERα/ERβ (estrogen receptors), GPER/GPR30 (membrane estrogen receptor), PR (progesterone receptor), Cyclin D1 (cell cycle regulatory protein), PI3K, Akt, MAPK (ERK), ERE (estrogen response element), CYP19A1 (aromatase), FOXO1 (bone metabolism regulatory transcription factor), Bcl-2 (anti-apoptotic protein).
Core key proteins: Estrogen (E2, 17β-estradiol), ERα/ERβ (estrogen receptors), GPER/GPR30 (membrane estrogen receptor), PR (progesterone receptor), Cyclin D1 (cell cycle regulatory protein), PI3K, Akt, MAPK (ERK), ERE (estrogen response element), CYP19A1 (aromatase), FOXO1 (bone metabolism regulatory transcription factor), Bcl-2 (anti-apoptotic protein).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us