- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

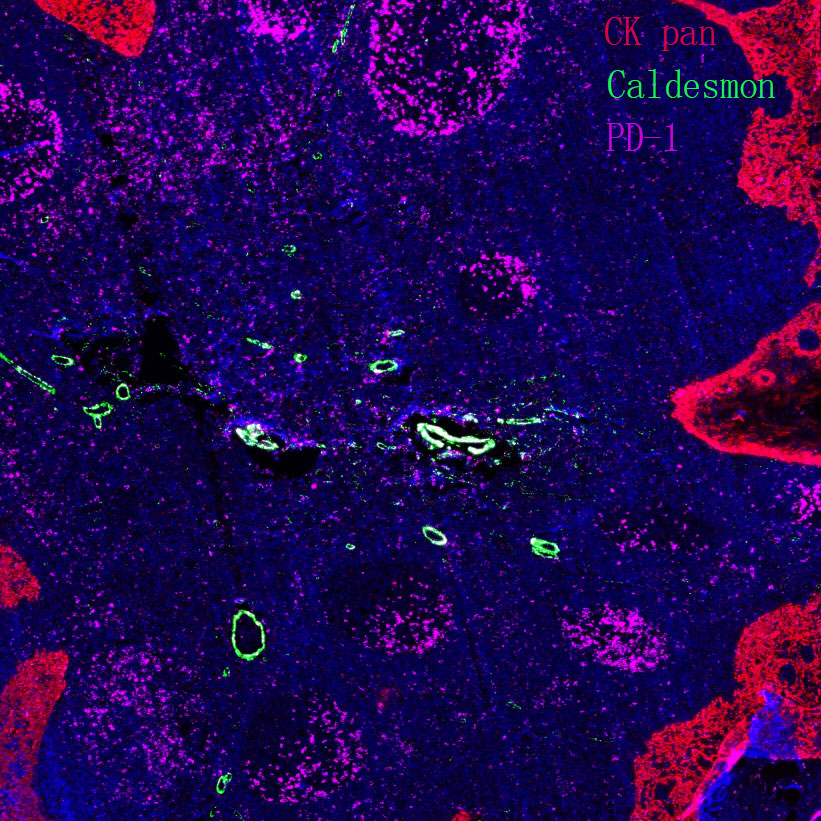
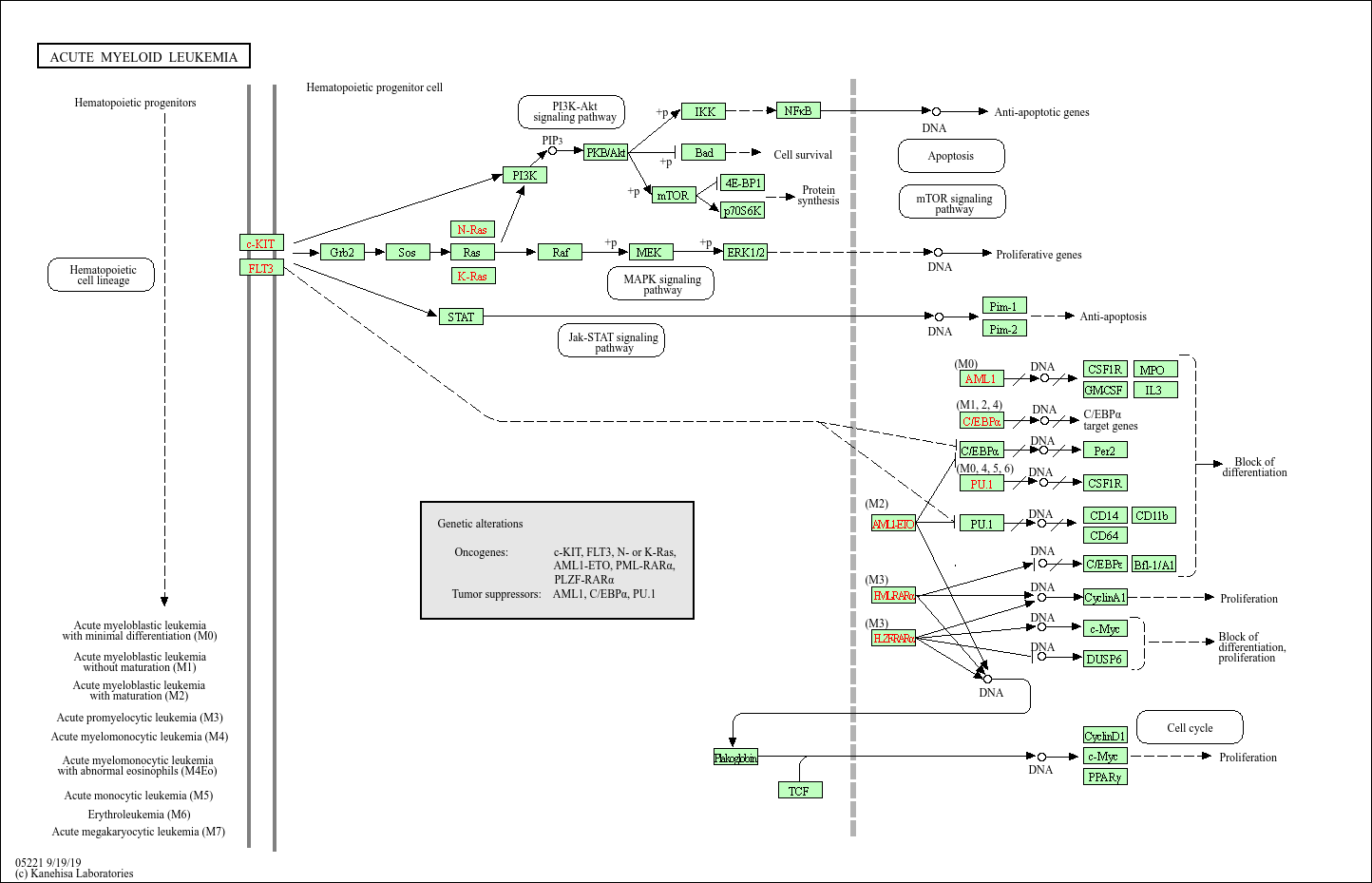
Acute myeloid leukemia
Core of basic research: Focus on the molecular mechanisms underlying the malignant transformation of myeloid hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells, with key drivers being differentiation arrest and uncontrolled proliferation induced by genetic variations. Core research directions include the function of fusion proteins generated by chromosomal translocations (e.g., t(15;17)), the signal activation mechanism of kinase mutations (e.g., FLT3-ITD), and the development of targeted drugs against these abnormal molecules.
Core key proteins: FLT3 (sustained activation of proliferation signals upon mutation), PML-RARα fusion protein (blocks myeloid differentiation), RUNX1 (key transcription factor for hematopoietic differentiation), CEBPA (regulates myeloid cell maturation), c-KIT (stem cell factor receptor, enhanced survival signals upon mutation), TP53 (tumor suppressor gene, inactivation promotes tumor progression).
Core key proteins: FLT3 (sustained activation of proliferation signals upon mutation), PML-RARα fusion protein (blocks myeloid differentiation), RUNX1 (key transcription factor for hematopoietic differentiation), CEBPA (regulates myeloid cell maturation), c-KIT (stem cell factor receptor, enhanced survival signals upon mutation), TP53 (tumor suppressor gene, inactivation promotes tumor progression).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us