- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

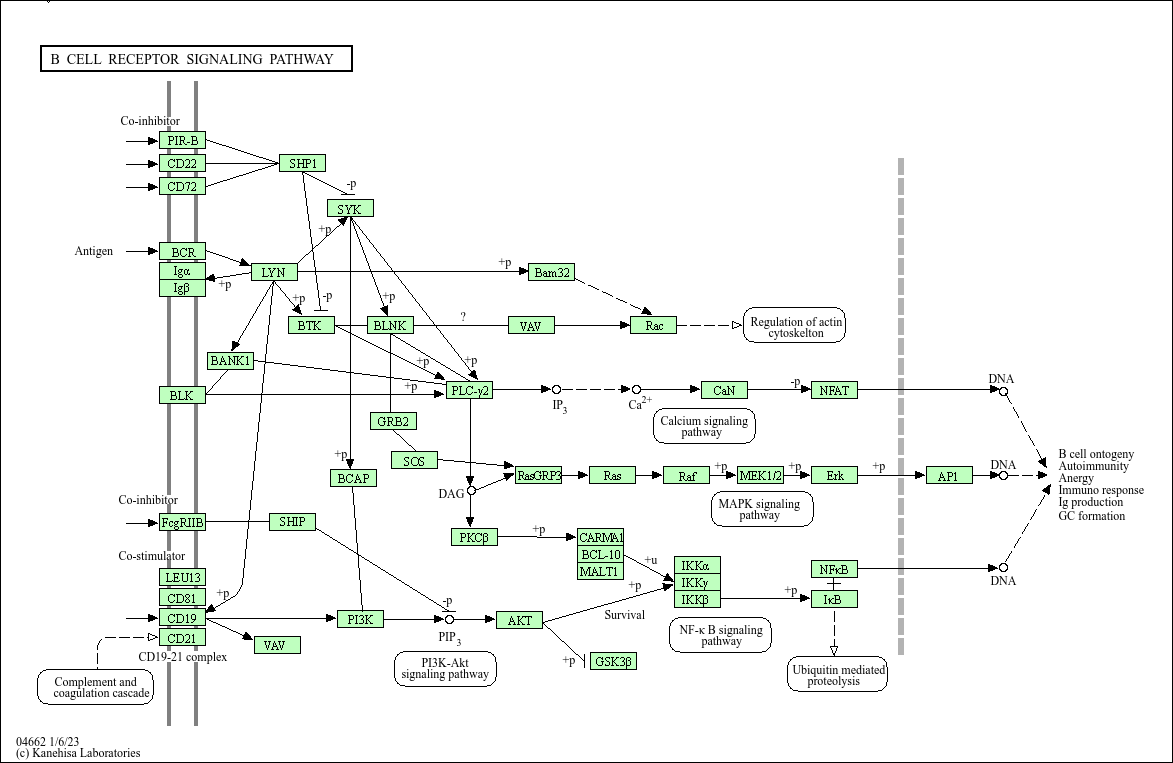
B cell receptor signaling pathway
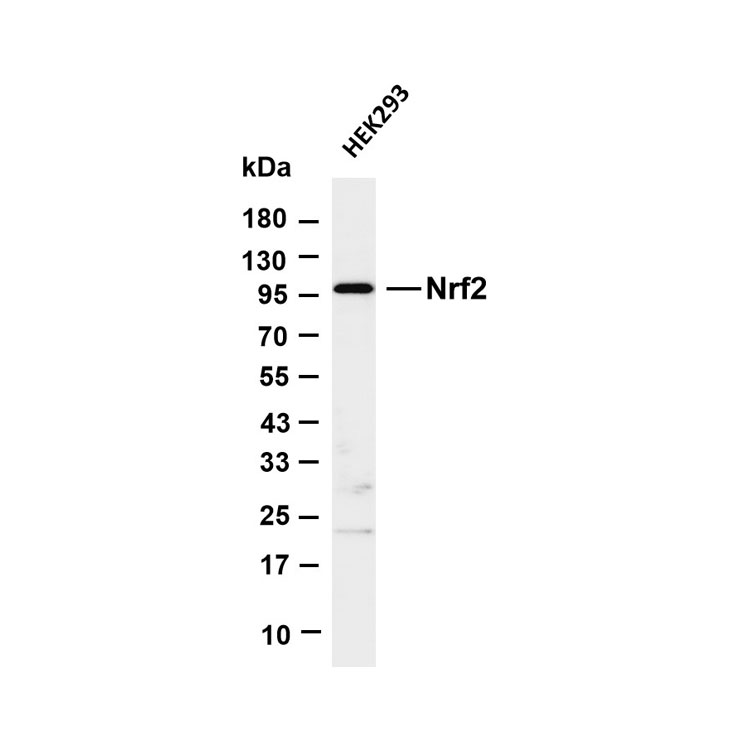
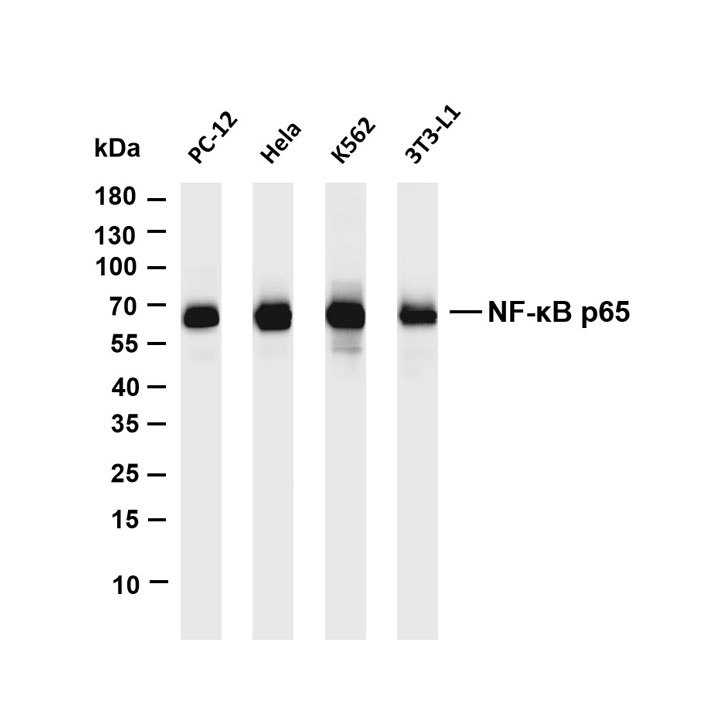
Core of basic research: It deciphers the signal cascade initiated by B cells recognizing antigens via BCR, which is critical for B cell proliferation and differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells or memory B cells. After BCR binds to antigens, the ITAM motifs in the cytoplasmic domains of CD79a/CD79b are phosphorylated by Src family kinases such as Lyn, recruiting and activating Syk kinase. This further triggers two core signal branches: ① PLC-γ2 hydrolyzes PIP2 to generate IP3 and DAG, where IP3 promotes calcium influx and DAG activates PKC, ultimately activating NF-κB; ② The PI3K-Akt pathway inhibits apoptosis and promotes metabolic reprogramming. Research focuses on the mechanism of immune synapse formation, phosphorylation cascade regulation of signaling molecules (e.g., the role of negative regulator SHIP1), synergistic enhancement of the pathway by cytokines (IL-4, IL-6), and molecular mechanisms of abnormal BCR activation (e.g., recognition of self-antigens) in autoimmune diseases.
Core key proteins: BCR complex (IgM/IgD + CD79a/CD79b), Lyn, Syk (tyrosine kinases), PI3K, Akt, PLC-γ2, IP3R (calcium channel), PKC, NF-κB, STAT3, SHIP1 (negative regulator), BLNK (signal adaptor protein).
Core key proteins: BCR complex (IgM/IgD + CD79a/CD79b), Lyn, Syk (tyrosine kinases), PI3K, Akt, PLC-γ2, IP3R (calcium channel), PKC, NF-κB, STAT3, SHIP1 (negative regulator), BLNK (signal adaptor protein).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us