- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

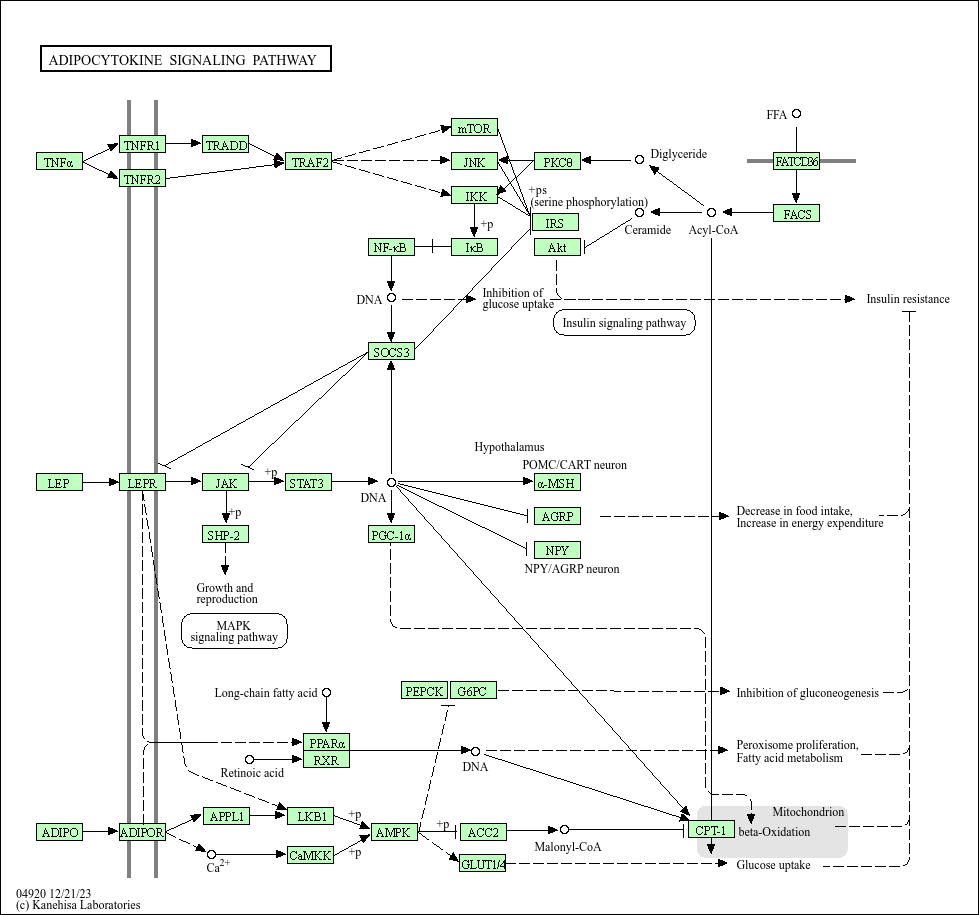
Adipocytokine signaling pathway
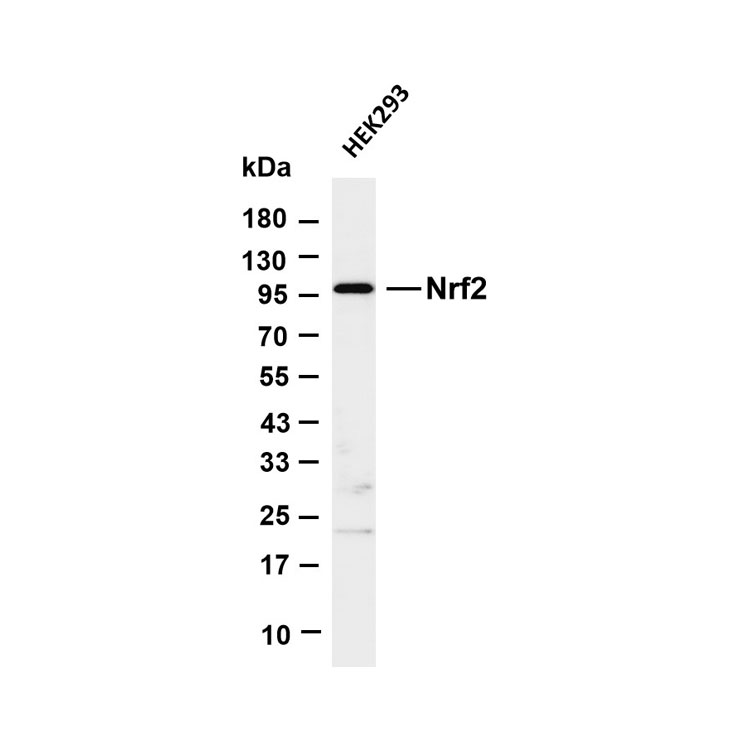
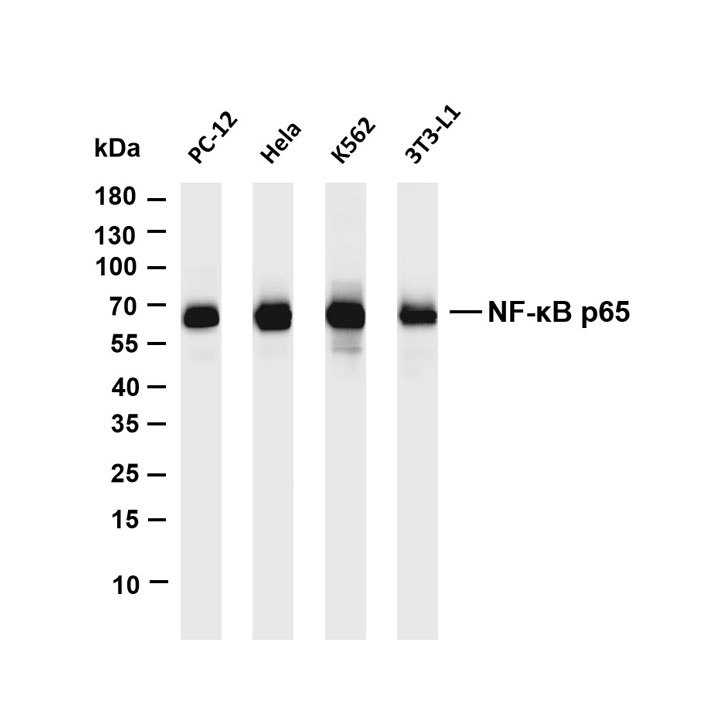
Core of basic research: A key pathway linking adipose metabolism and systemic homeostasis, focusing on the molecular mechanisms by which adipocytokines secreted by adipocytes regulate glucose/lipid metabolism, inflammation, and energy balance. Adipocytokines are classified into pro-inflammatory (e.g., Leptin, Resistin) and anti-inflammatory (e.g., Adiponectin, Omentin) types, acting on target organs (liver, muscle, pancreas, blood vessels) via autocrine, paracrine, or endocrine modes. Leptin binds to the leptin receptor (Ob-R) to activate the JAK2-STAT3 pathway, inhibiting appetite and promoting energy expenditure. Adiponectin binds to AdipoR1/AdipoR2, activating the AMPK or PPARα pathway to improve insulin sensitivity and promote fatty acid oxidation. Resistin induces chronic inflammation via activating the NF-κB pathway, exacerbating insulin resistance. Research focuses on the regulatory network of adipocytokine secretion, synergistic/antagonistic effects among different factors, and pathway abnormalities associated with metabolic syndrome (obesity, type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia) and cardiovascular diseases.
Core key proteins: Leptin, Adiponectin, Resistin, Omentin, Ob-R (leptin receptor), AdipoR1/AdipoR2 (adiponectin receptors), JAK2, STAT3, AMPK, PPARα, NF-κB, IRS1/2 (insulin receptor substrates), GLUT4 (glucose transporter).
Core key proteins: Leptin, Adiponectin, Resistin, Omentin, Ob-R (leptin receptor), AdipoR1/AdipoR2 (adiponectin receptors), JAK2, STAT3, AMPK, PPARα, NF-κB, IRS1/2 (insulin receptor substrates), GLUT4 (glucose transporter).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us